Himalaya
Physiological Division of India
On the basic of relief feature or geomorphology or topography India is physically divided in to following six parts.
1. Mountain region of India.
2. Plains of River Ganga
3. Peninsular region of India.
4. Thar Desert
5. Coastal region of India.
6. Island region of India.
The Himalayan Mountains
Himalayan Mountain Range is the highest mountain range of the world.
The Himalayan Range it's the third longest range of the world after Andes and Rockies.
The average elevation of the Himalaya is around 6000 meters.
The highest Peak of the Himalaya and the word is Everest, located in Nepal where it is also called as Sagarmatha.
Himalaya it's called Chomolungma in Tibet.
Second highest peak of the world is K2 or Godwin (8611mt.) Austen, which is also the highest peak of India, located in Kashmir.
Third highest peak of the world and second highest peak of the India is Kanchanjangha, located in the Sikkim.
Eastern most peak of Himalaya is Namcha Barwa, located in Arunachal Pradesh.
The narrow ways located between two mountain ranges or hills which provides transportation are called ‘pass’ or ‘gapes’. Some important passes located in Himalaya are-
Banihal Pass, connect to the mountain areas of Kashmir valley and Jammu.
Karakoram Pass is located in Karakoram Range, connect China and India.
Zoji La Pass is located between Kashmir Valley and Kargil District and it is the only way to enter in Laddakh from west.
Rohtang Pass is located in Himachal Pradesh, India.
Mohan Pass is Located in Shiwalik Hill
Kora La Pass is located in Nepal-Sikkim border on 4,594-meter height.
In Sikkim Nathu La and Jalep La Passes connect Gangtok to Lhasa in Tibet.
Sir Sidney Burrard has given the lateral classification of the Himalaya on the basis of the antecedent rivers as follows.



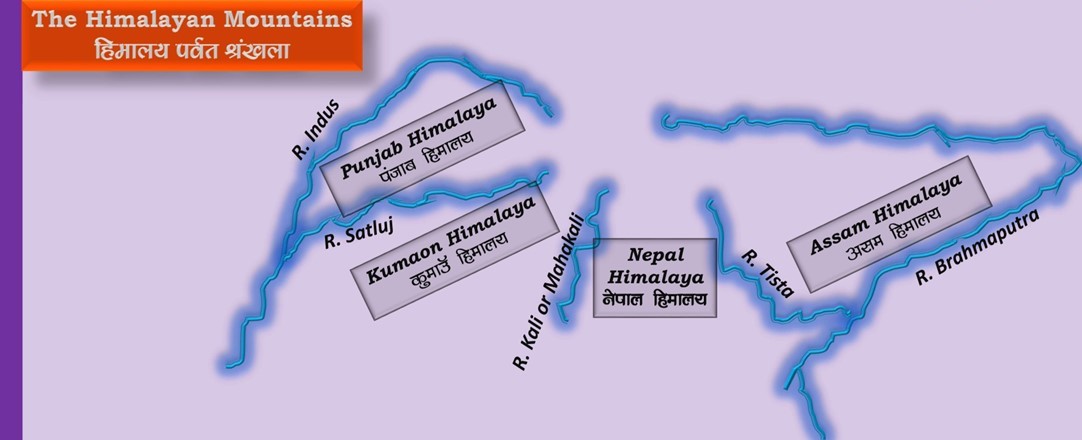



Comments